Advertisement
An AI-powered humanoid robot company has just raised $350 million, capturing global attention as it pushes the boundaries of what machines can do alongside humans. The idea of robots that walk, talk, and respond like people has moved from fiction to reality, and this investment shows how much faith investors have in its future.
These human-like machines are no longer just prototypes tucked away in labs—they’re being designed to work in stores, hospitals, and warehouses. With this funding, the company plans to make its robots smarter, more approachable, and more useful in everyday situations where a human touch still matters.
Humanoid robots—machines designed to walk, gesture, and even speak like humans—have long fascinated engineers and the public. Their development was held back for years by clunky movements and limited AI. This company, however, has been quietly improving its designs and now stands out with machines that move more fluidly and communicate more naturally.

The $350 million comes from venture capital, tech-focused funds, and strategic partners in industries like logistics and healthcare. Investors are excited about how these robots could ease staff shortages in jobs requiring interaction, dexterity, and consistency. The company’s models are already being tested in retail, healthcare, and service roles. These robots use advanced AI models to process language, interpret context, and adjust their gestures to suit situations. The funding will help expand production, improve AI capabilities, and lower manufacturing costs.
Their robots stand out for their ability to follow spoken instructions in real-time, hold simple conversations, and respond to emotional cues. That has made them appealing to workplaces that need a human touch without relying entirely on human staff. The company's progress reflects how humanoid robotics is moving closer to becoming a part of everyday operations in certain industries.
The company has shared plans for using the $350 million. A large portion will fund a dedicated high-volume production facility. Building humanoid robots requires precision components—such as advanced sensors, flexible joints, and compact processors—that are still expensive to manufacture at scale. This facility is expected to reduce unit costs over time, making their robots more accessible to smaller businesses.
They will also invest heavily in research and development. While their robots already excel at basic tasks and interactions, they want to improve their ability to operate in unpredictable environments. Current models can move smoothly in controlled settings, but dynamic spaces—such as crowded hospital corridors or busy stores—pose a challenge. Upgraded perception and decision-making systems are a priority.
Another focus is emotional intelligence. The company’s AI can already detect certain emotions in speech and adjust tone or gestures accordingly. They now aim to expand these capabilities so their robots can recognize more subtle emotional cues, making interactions more meaningful. This could help robots feel less mechanical and more relatable, particularly in sensitive settings such as elder care or hospitality.
Finally, the company plans to partner with businesses to deploy robots in real-world pilot programs. These trials will provide insights into how people react to them, identify which features need refinement, and assess their performance over extended periods.
This investment highlights a broader trend toward integrating humanoid robots into workplaces. Advances in AI, along with falling costs for components, are making these machines more practical. One of their biggest advantages is that they can operate in environments designed for people without major adjustments. That makes them appealing to businesses that don’t want to redesign workflows just to adopt automation.

Healthcare facilities are already testing robots that assist with moving patients, delivering supplies, and offering companionship to those in long-term care. Retailers have begun using them to guide customers, answer questions, and handle checkout. Logistics companies see value in their flexibility to pick, pack, and move goods in warehouses that aren’t entirely automated.
People also tend to feel more comfortable around machines that look and behave like them. This company designs its robots with approachable features and calm voices, reducing hesitation among those interacting with them. The familiarity of a humanoid form can make the idea of automation less jarring, which helps acceptance in public and professional spaces.
Labor shortages are another reason for the growing interest. Many industries are struggling to find enough workers, especially for repetitive or physically demanding tasks. Humanoid robots can step in to support staff, taking over routine work and letting people focus on jobs that require decision-making or creativity. This helps explain why investors believe humanoid robotics will see growing demand in the years ahead.
Despite the enthusiasm, several challenges remain. Humanoid robots are still more expensive than traditional automation options, and their reliability in chaotic environments is not yet proven. The company is aware of these concerns and plans to use the funding to improve durability, intelligence, and adaptability.
Social and ethical questions also arise. Some worry about machines replacing jobs or about people forming unhealthy attachments to them. The company maintains that its robots are designed to assist, not replace, humans, and it is working on guidelines to ensure their responsible use.
The coming years will be telling. The company expects to roll out large pilot programs over the next year and make its robots more widely available soon after. If successful, humanoid robots could shift from being experimental to becoming familiar fixtures in workplaces and public spaces.
The $350 million funding signals a strong belief in the future of AI-powered humanoid robots. With plans to refine technology, scale production, and test real-world use, the company is moving closer to making these machines part of daily life. Designed to support rather than replace people, their robots show how humanoid robotics can fit naturally into workplaces and public spaces. This investment marks a meaningful step toward a world where humans and intelligent machines work side by side.
Advertisement

How MobileNetV2, a lightweight convolutional neural network, is re-shaping mobile AI. Learn its features, architecture, and applications in edge com-puting and mobile vision tasks

Beginner's guide to extracting map boundaries with GeoPandas. Learn data loading, visualization, and error fixes step by step

Why is Alibaba focusing on generative AI over quantum computing? From real-world applications to faster returns, here are eight reasons shaping their strategy today
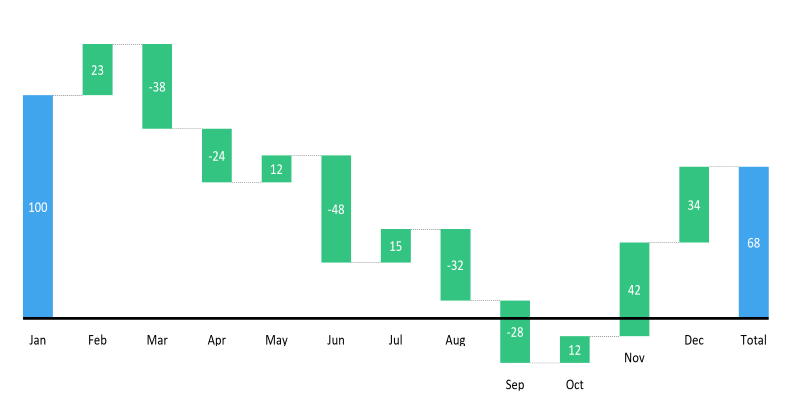
Learn how to create a waterfall chart in Excel, from setting up your data to formatting totals and customizing your chart for better clarity in reports

Google's Willow quantum chip boosts performance and stability, marking a big step in computing and shaping future innovations

What happens when an automaker lets driverless cars loose on public roads? Nissan is testing that out in Japan with its latest AI-powered autonomous driving system

What happens when blockchain meets robotics? A surprising move from a blockchain firm is turning heads in the AI industry. Here's what it means

Is the UK ready for AI’s energy demands? With rising power use, outdated cooling, and grid strain, the pressure on data centers is mounting—and sustainability may be the first casualty

How the ORDER BY clause in SQL helps organize query results by sorting data using columns, expressions, and aliases. Improve your SQL sorting techniques with this practical guide
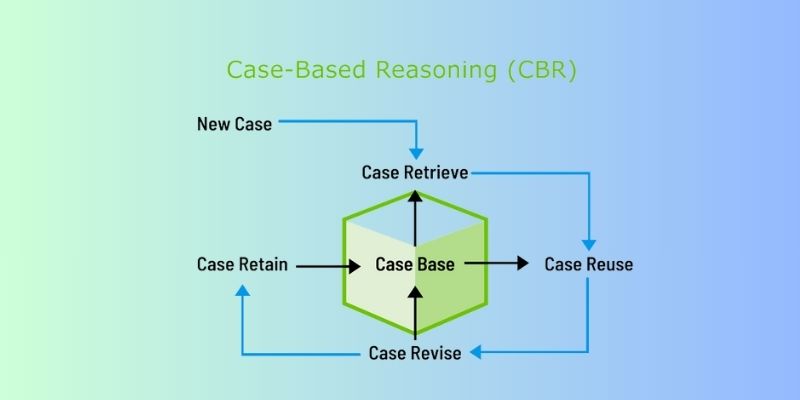
Discover how Case-Based Reasoning (CBR) helps AI systems solve problems by learning from past cases. A beginner-friendly guide

What happens when robots can feel with their fingertips? Explore how tactile sensors are giving machines a sense of touch—and why it’s changing everything from factories to healthcare

SmolVLM2 brings efficient video understanding to every device by combining lightweight architecture with strong multimodal capabilities. Discover how this compact model runs real-time video tasks on mobile and edge systems