Advertisement
Successful operations require a clear understanding of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and business process management (BPM). While these tools serve distinct purposes, both offer powerful solutions for improving efficiency. RPA focuses on automating repetitive, rule-based tasks, whereas BPM is designed to optimize and manage entire business processes. Knowing when and how to apply each approach is critical—misuse or confusion between the two can lead to wasted resources and subpar results.
Although often conflated, RPA and BPM are best suited to specific objectives, and applying them appropriately can improve process flow, enhance compliance, reduce costs, and drive operational efficiency. Evaluating them side by side helps clarify their role in digital transformation. Professionals must understand how each tool contributes to automation strategies and business growth. By exploring their differences, organizations can make informed decisions that support long-term success.
Robotic process automation (RPA) automates repetitive, rule-based activities using software bots that mimic human actions within digital systems. Companies use RPA for customer support, invoice processing, and data entry tasks. Bots enhance accuracy and speed by eliminating human delays. RPA typically works without requiring changes to existing systems, operating on top of them. Faster work completion and fewer human mistakes help companies.
Employees are freed from routine, repetitive tasks. Instead, they can concentrate on value-driven projects. RPA is particularly useful in finance, HR, and IT departments. Usually, quick implementation provides speedy returns. However, RPA is less effective with unstructured or judgment-based processes. It performs better on well-defined, rule-based chores. Maintaining bot scripts and logic is essential for scalability. For short wins in digital automation, it's perfect. RPA functions more as a workforce extension than as a complete process reform. Knowing its extent guarantees correct implementation for companies' workflow automation systems.

Business process management (BPM) focuses on improving end-to-end business processes. It involves mapping, analyzing, and optimizing departmental workflows. BPM enhances process visibility, regulatory compliance, and overall efficiency. Unlike RPA, BPM is a long-term, strategic approach to process improvement. It often requires reengineering existing systems and workflows. BPM solutions help organizations monitor workflows, identify inefficiencies, and drive innovation. BPM is well-suited for managing complex, cross-functional business operations. It promotes process standardization and cross-team collaboration. BPM systems often include modeling, automation, and analytics tools.
These tools offer insights into process performance and bottlenecks. Real-time data enables speedy decision-making. BPM supports continuous, incremental improvement over time. It finds application in manufacturing, service, healthcare, and logistics. BPM may interface via APIs with many different systems. It guarantees processes in line with corporate objectives. Selecting BPM helps to create flexible and scalable processes. Digital transformation has a solid basis for this. Businesses looking for whole lifecycle management should give BPM top importance. It helps long-term compliance and efficiency in tools for process optimization.
RPA and BPM differ in purpose, scope, and application. RPA focuses on automating individual tasks. BPM manages entire business processes from start to finish. RPA manages rule-based, repeated tasks using bots. BPM is revamping and analyzing whole processes. RPA enables rapid deployment and immediate results. Often taking more time, BPM requires more planning. RPA integrates without needing system modifications. BPM might call for integrations or system changes. RPA works best for structured tasks such as data migration. BPM handles complex scenarios involving multiple systems or departments. While RPA reduces manual effort, it doesn't improve process structure.
BPM seeks to maximize and simplify business flows. RPA discreetly runs in the background doing chores. BPM typically involves dashboards and user interfaces for monitoring and control. In contrast, RPA is more tactical, handling specific tasks without altering broader workflows. BPM, on the other hand, serves a strategic role by shaping end-to-end process improvements. They fulfill several automated purposes. Knowledge of these variations helps to prevent ambiguity. The correct strategy will rely on your objectives. Aligning tools with your entire workflow automation strategy for businesses will help you to maximize benefits.
RPA is ideal for time-consuming, repetitive, and rules-based tasks, such as email responses, form processing, and data entering. It boosts speed and accuracy without altering existing systems. It's ideal for small automation projects with quick ROI. RPA fits companies wanting efficiency with little disturbance. Use BPM when you need to redesign or manage entire systems and workflows. BPM performs effectively for process oversight, compliance audits, and cross-departmental projects. BPM tracks performance, notes mistakes, and enhances output.
Additionally, supported by BPM is scalable automation. It gets your company ready for the demands of tomorrow. BPM provides structure in case your process is faulty or invisible. In some cases, both RPA and BPM are needed in tandem. RPA may manage tasks inside a BPM-run system. Using hybrid technologies enhances outcomes. Using each tool at the right moment guarantees better decisions. Correspond the tool to your goal. Understanding each tool prevents wasted effort and resources. Always match your decision with general process optimization tools and benefits for the best effects.
RPA and BPM are complementary technologies, not competing technologies. BPM outlines the course of the process, while RPA runs the little chores contained within it. Taken in concert, they increase workflows and boost output. BPM offers structure and surveillance, while RPA offers precision and speed. Integration makes smart automation possible. Together, they deliver both macro and micro-level improvements. BPM points out areas where RPA bots can be valuable. RPA manages data flows between several applications. Real-time process adjustments via BPM drive continuous improvement.
Using both tools maximizes return on investment. It generates evolving end-to-end automation throughout time. This integration increases compliance and lessens hand-work. Companies obtain scalability and flexibility. Over time, combining tools also helps to save expenses. Teams work smarter, not harder. It improves your whole workflow automation strategy for businesses. Growing digital demands integrated technologies future-proof your operations. Leaders must embrace both if they are nimble and competitive in the continually shifting terrain of markets.
Understanding the differences between RPA and BPM helps organizations choose the right automation solution. RPA shines on straightforward, repetitious tasks. BPM is mostly concerned with streamlining whole procedures. Both tools have merit in distinct respects. Combining them yields more advantages. Long-term success depends on matching your tools with corporate objectives. Good integration increases output and streamlines processes. Making wise decisions enhances your business flow automation plan. Always match the correct tool to your requirements. In contemporary corporate settings, that choice promotes resilience, efficiency, and growth. Stay educated to release real digital transformation possibilities.
Advertisement
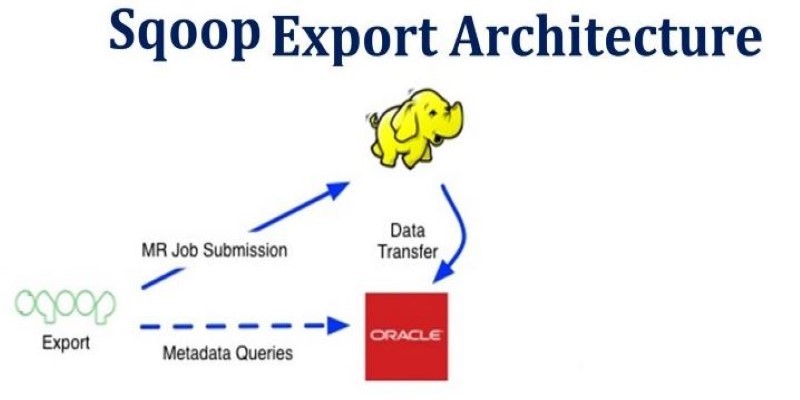
How Apache Sqoop simplifies large-scale data transfer between relational databases and Hadoop. This comprehensive guide explains its features, workflow, use cases, and limitations
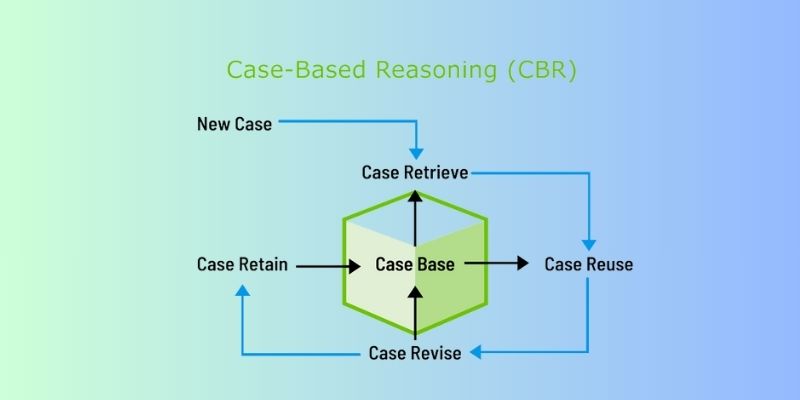
Discover how Case-Based Reasoning (CBR) helps AI systems solve problems by learning from past cases. A beginner-friendly guide

What happens when robots can feel with their fingertips? Explore how tactile sensors are giving machines a sense of touch—and why it’s changing everything from factories to healthcare

Learn the top eight impacts of global privacy laws on small businesses and what they mean for your data security in 2025.

Artificial Superintelligence represents a stage where machines surpass human intellect in creativity, logic, and awareness. Learn how this emerging form of intelligence could transform science, society, and the way humans define consciousness in a rapidly evolving world
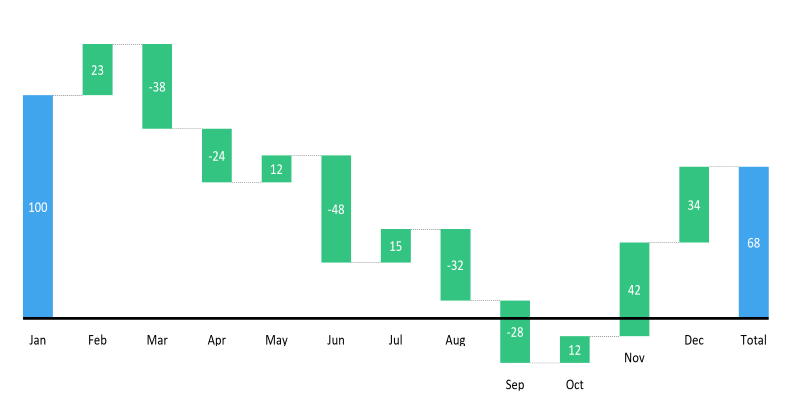
Learn how to create a waterfall chart in Excel, from setting up your data to formatting totals and customizing your chart for better clarity in reports
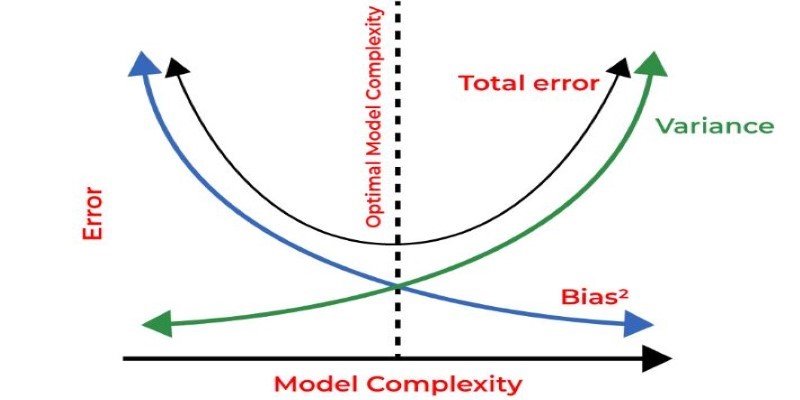
How regularization in machine learning helps prevent overfitting and improves model generalization. Explore techniques like L1, L2, and Elastic Net explained in clear, simple terms

If you want to assure long-term stability and need a cost-effective solution, then think of building your own GenAI applications

How the ORDER BY clause in SQL helps organize query results by sorting data using columns, expressions, and aliases. Improve your SQL sorting techniques with this practical guide

How MobileNetV2, a lightweight convolutional neural network, is re-shaping mobile AI. Learn its features, architecture, and applications in edge com-puting and mobile vision tasks

What Amazon Bedrock is and how AWS’s generative AI service helps businesses access powerful foundation models, customize AI applications, and simplify integration through a single platform

How to Integrate AI in a Physical Environment through a clear, step-by-step process. This guide explains how to connect data, sensors, and software to create intelligent spaces that adapt, learn, and improve over time