Advertisement
AI tools are popping up all over the place, and if you're keeping tabs on what's happening in the cloud space, you've probably heard about Amazon Bedrock. It's not a buzzword or just another AWS service tucked into their growing list. Bedrock is Amazon's take on making generative AI more accessible, flexible, and deeply integrated with cloud applications without forcing developers to deal with heavy infrastructure or model training. That might sound like marketing fluff, but it's a smart move that lowers the technical barrier for companies wanting to build AI into their apps. Here's what that really means.
Amazon Bedrock is a managed service that gives developers access to foundational models (FMs) from various AI model providers through a simple API. These aren’t just any models—they include some of the most well-known names in the space, like Anthropic (Claude), AI21 Labs (Jurassic), Meta (Llama), Stability AI, and Amazon's own Titan models. Bedrock lets developers choose among these without having to manage infrastructure, provision GPUs, or fine-tune large language models from scratch.

This approach matters. Large language models require immense computing resources and expertise to train or customize. Most businesses can’t afford that or don’t want to manage the risks. With Bedrock, a team can pick a model, connect it to their app via an API, and start generating summaries, answering questions, translating content, creating images, or even building chatbots. All of this is done within the AWS ecosystem, which many companies are already using.
Customization is a big part of the offering. While you don't have to train a model from scratch, you can still adapt it to your needs. Amazon supports a technique called "fine-tuning" through prompts and data without ever exposing your proprietary data to the model provider. That means your data stays in your control, a concern many companies have when it comes to using third-party models.
One of the common concerns about using AI platforms is vendor lock-in. Bedrock was designed with that in mind. Since it gives access to multiple foundation models, you're not locked into a single AI vendor. If you want to use Anthropic’s Claude today and try out Amazon Titan next month, you can do that. If one model performs better for summarization and another is better at open-ended generation, you can switch between them or even use them in parallel.
This plug-and-play setup is especially useful for developers who want to experiment. Each model provider has its strengths and nuances. Some models handle longer context windows better; others are stronger in reasoning or structured generation. Bedrock doesn’t force you to choose one early and stick with it forever.
Another key advantage is integration. Since it’s a native AWS service, Bedrock connects easily with other AWS tools. If you’re storing data in Amazon S3, running applications on Lambda, or managing workflows in Step Functions, Bedrock fits in neatly. That saves time and avoids the need to stitch together services with custom code.
While a lot of attention goes to flashy AI demos, Amazon Bedrock focuses on practical enterprise use. Businesses use it to build internal tools, automate customer service, generate content for websites, and even build custom AI assistants. It supports text and image generation, summarization, question answering, and natural language search.

A real-world example: A retail company could use Bedrock to create a chatbot that helps customers find products, answers questions about return policies, and even generates promotional copy for new items. All of this can be done using foundation models accessed through Bedrock—no model training, no GPU clusters, and no need to wrangle API rate limits across different model vendors.
Compliance is another piece. Since many of the customers using AWS are regulated businesses, Amazon makes sure Bedrock fits within security frameworks. Your data doesn't leave your AWS environment, and you can monitor usage just like you would any other AWS resource. This gives IT teams more visibility and confidence compared to using external APIs from startups.
Amazon arrived a little later to the generative AI conversation compared to OpenAI or Google, but Bedrock shows that it's playing a long-term game. Instead of building a single flagship model and expecting everyone to use it, Amazon is acting more like an AI marketplace. It's saying: here are multiple tools, pick what works for you, and we’ll make it easy to use them.
That positions Bedrock as a neutral ground, which is a smart bet. Many businesses don’t want to take a risk on a single provider or shift their entire tech stack to follow one AI trend. With Bedrock, they get flexibility, enterprise-grade reliability, and choice.
At the same time, Amazon is investing heavily in its own Titan models, which are optimized to work smoothly with Bedrock and other AWS tools. Titan includes models for text generation, embedding, and other tasks that match what you'd expect from a modern LLM. These models will likely continue to grow in capability and serve as a strong default for companies that don't have preferences.
As demand for AI grows, Bedrock provides AWS with another way to stay relevant in a space increasingly defined by models and data, rather than just compute and storage. It reflects a shift in what the cloud means. It's not just where you run your software anymore, it's where you access intelligence.
Amazon Bedrock isn’t loud. It didn’t debut with the same buzz as ChatGPT or Gemini, but it doesn’t have to. Its strength is in its practical design that focuses on usability over hype. Bedrock helps teams build AI-driven tools that quietly improve products rather than dominate them. By providing access to top-tier models, keeping everything serverless and API-based, and blending seamlessly with the AWS ecosystem, Bedrock makes generative AI practical for real business use. Whether you’re testing a chatbot or adding AI to your workflow, it removes complexity and friction. It’s simple, steady, and works—exactly why it stands out.
Advertisement

Learn about landmark legal cases shaping AI copyright laws around training data and generated content.

Understand how GPT's decoder-only transformer works, its advantages, challenges, and why it is transforming the future of AI
Discover how AI in the construction industry empowers smarter workflows through Industry 4.0 construction technology advances

If you want to assure long-term stability and need a cost-effective solution, then think of building your own GenAI applications
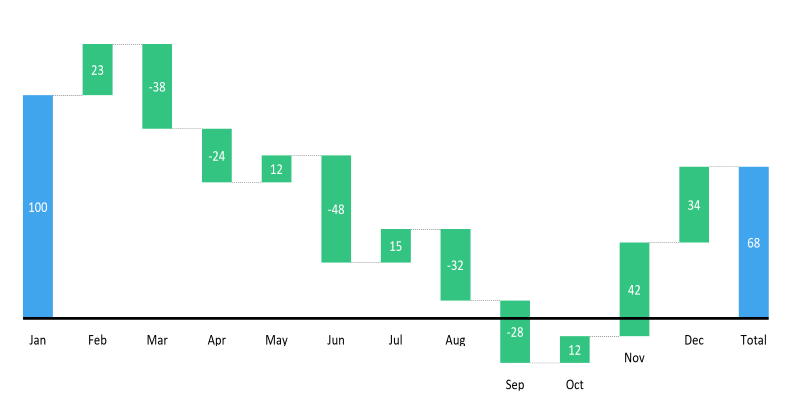
Learn how to create a waterfall chart in Excel, from setting up your data to formatting totals and customizing your chart for better clarity in reports

Which data science companies are actually making a difference in 2025? These nine firms are reshaping how businesses use data—making it faster, smarter, and more useful

Can a robotic puppy really help ease dementia symptoms? Investors think so—$6.1M says it’s more than a gimmick. Here’s how this soft, silent companion is quietly transforming eldercare

Google's Willow quantum chip boosts performance and stability, marking a big step in computing and shaping future innovations

Learn the top eight impacts of global privacy laws on small businesses and what they mean for your data security in 2025.

How to Integrate AI in a Physical Environment through a clear, step-by-step process. This guide explains how to connect data, sensors, and software to create intelligent spaces that adapt, learn, and improve over time

How agentic AI is driving sophisticated cyberattacks and how the UK AI Opportunities Action Plan is shaping industry reactions to these risks and opportunities

How the EV charging industry is leveraging AI to optimize smart meter data, predict demand, enhance efficiency, and support a smarter, more sustainable energy grid